Training large language models, generating images, and analyzing video — these core AI workloads run on powerful GPUs. While these accelerators are the cornerstone of modern AI, they represent a significant and often unpredictable portion of AI infrastructure costs. Without a strategic approach, your cloud GPU spending can quickly spiral out of control.
This guide will explore practical strategies to maximize the value of every dollar you invest in compute, significantly reducing GPU costs without sacrificing performance.
Why is GPU Computing So Expensive? Understanding AI Infrastructure Costs
The price of a single professional-grade NVIDIA H100 or A100 GPU can be substantial. However, the acquisition cost is only part of the equation. To run effectively, these chips require a costly supporting ecosystem:
- High-performance servers for maximum data throughput
- Robust power supplies, as high-end setups consume kilowatts of energy
- Advanced cooling systems to maintain safe operating temperatures
This leads to a critical question: why not use cheaper, consumer-grade GPUs? The answer lies in reliability and optimization. Data center GPUs are engineered for 24/7 operation, feature Error-Correcting Code (ECC) memory to prevent data corruption, and are licensed for commercial use. More importantly, only professional accelerators like the H100 and A100 can be efficiently clustered to train the massive models powering today's generative AI.
Finally, the generative AI boom has created a massive supply shortage, driving up prices for both hardware and cloud GPU instances. Without a systematic approach to GPU cost management, your budget can easily derail.
Right-Size Your GPU: Match the Hardware to Your AI Workload
Using a top-tier NVIDIA H100 for every task is a classic example of poor GPU resource management. The most impactful step in optimizing GPU costs is right-sizing—matching the hardware to the specific workload.
The key is understanding the difference between model training and model inference:
- Training AI Models: This process of building a model from scratch demands maximum computational power. High-performance accelerators like the NVIDIA H100 are essential for processing vast datasets over weeks or months.
- Running Model Inference: This is the act of using a trained model, such as processing a user's prompt. Here, the focus shifts to latency, throughput, and cost-efficiency. For inference, cards like the NVIDIA L4 or T4 are ideal for handling high request volumes cost-effectively. Versatile solutions like the NVIDIA L40S also offer a strong balance for both fine-tuning and complex inference.
Pro Tip: Audit your current GPU usage to identify mismatches. You may find that 70% of your inference workloads could run on more cost-effective GPU instances.
Monitor and Optimize GPU Utilization
Even a correctly chosen GPU won't save you money if it sits idle. A powerful server with low GPU utilization is a direct drain on your budget. Effective cloud cost optimization requires getting a handle on your resource management.
Audit Your Current GPU Usage
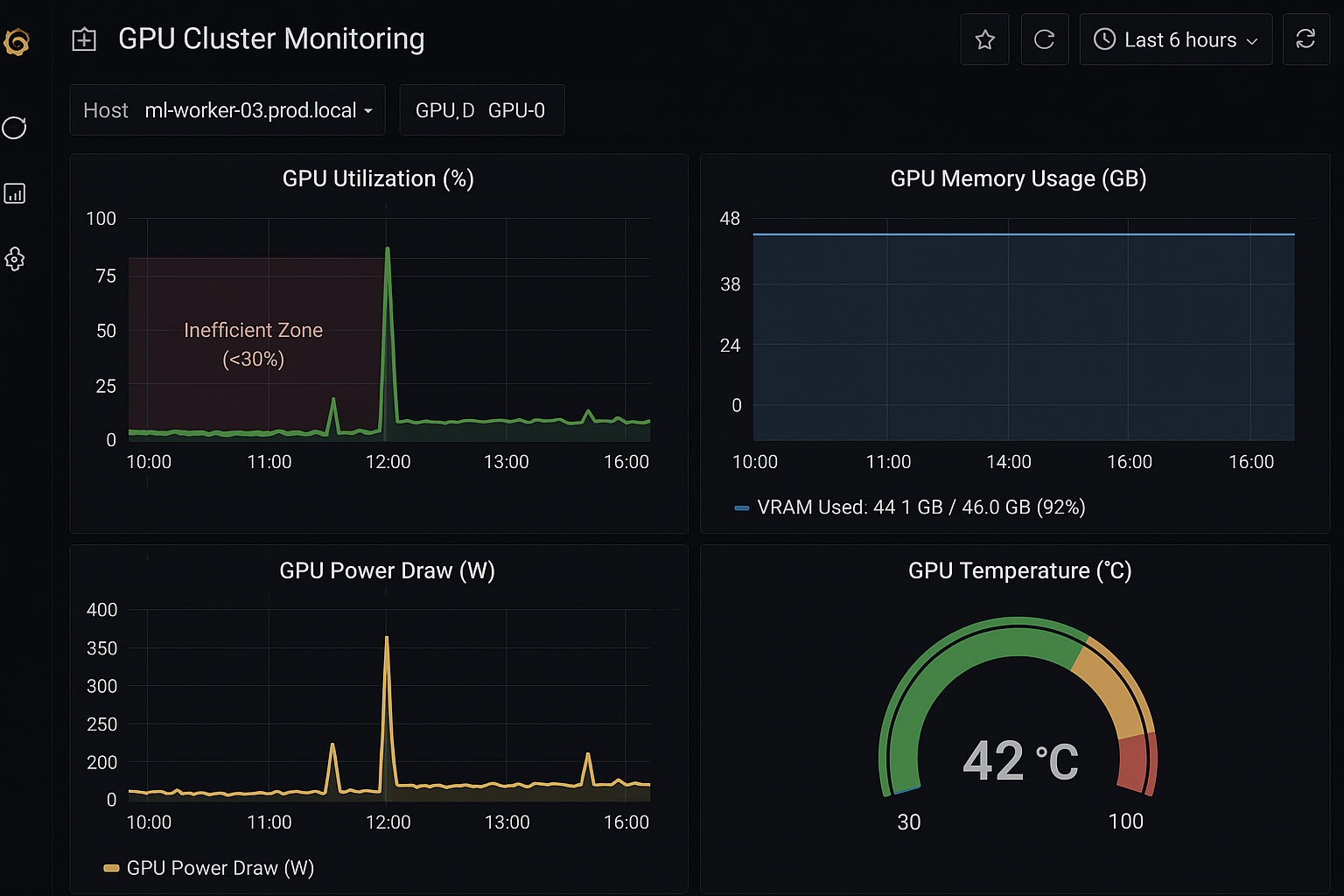
Start by running nvidia-smi on your machines or setting up a basic Grafana dashboard. If your GPU utilization is consistently below 80-90%, you are not getting full value from your investment.
Plan and Schedule AI Workloads
Move away from ad-hoc job launches by implementing a structured task queue. For better cluster utilization, schedule long, resource-intensive model training sessions for nights or weekends when demand is lower. This reserves peak-hour capacity for business-critical workloads.
Automate GPU Instance Shutdown
A major source of waste is cloud instances that run idle after jobs complete. Configure automated shutdown procedures to terminate instances immediately upon task completion, a key practice for managing cloud costs.
Share GPU Resources with Virtualization
When running multiple projects, avoid dedicating a physical GPU to each. Instead, leverage GPU virtualization technologies like NVIDIA MIG (Multi-Instance GPU) or orchestrate access with Kubernetes. This allows a single accelerator to serve multiple tasks, dramatically increasing utilization and reducing total cost.
Select the Optimal Compute Environment
Your choice of environment—cloud, on-premises, or a mix—is a strategic decision that directly impacts agility and total cost of ownership (TCO).
Leverage Managed AI/ML Platforms
Building your own Kubernetes cluster demands significant time, investment, and specialized DevOps skills. Managed AI services offer a compelling alternative with pre-configured, optimized infrastructure. A solution like a pre-configured Cloud4Y GPU server allows your team to bypass complex setup and focus on data science and model development, accelerating time-to-market.
Adopt a Hybrid Cloud Strategy
For companies with existing hardware, a hybrid cloud approach offers the best balance of control and flexibility. Run constant, baseline workloads on your reliable on-premises servers, and seamlessly burst to the cloud to handle peak demand or temporary experiments. This model combines the cost-effectiveness of owned hardware with the near-limitless scalability of the cloud.
Master Spot Instances for Fault-Tolerant Workloads
One of the most powerful levers for reducing cloud compute costs is leveraging spot instances (also known as preemptible VMs). These allow access to the same GPUs at discounts of 60-90% compared to on-demand pricing.
The trade-off is that the cloud provider can reclaim these instances with little warning. However, this model is highly effective for fault-tolerant AI workloads. If your training can be interrupted and resumed from a checkpoint, work can continue with minimal disruption.
Ideal use cases for spot instances include:
- Training with Frequent Checkpoints: Save progress every 15-30 minutes. The worst-case scenario is losing minutes of work, not days.
- Distributed Model Training: In a large cluster, losing a few instances does not halt the entire process.
- Time-Insensitive Tasks: Perfect for R&D, experiments, and processing large background datasets.
While using spot instances requires a resilient architecture, they are a cornerstone of an economically efficient AI infrastructure.
Key Takeaways for AI/ML Cost Optimization
- Right-size GPU resources to match specific workload requirements
- Monitor utilization and implement automated shutdown procedures
- Leverage GPU virtualization to increase resource utilization
- Consider hybrid cloud strategies for optimal TCO
- Use spot instances for fault-tolerant workloads to save 60-90%
Conclusion
Optimizing GPU costs is about building a culture of efficient resource consumption. It's a journey from asking "Which GPU?" to implementing a fully automated system where hardware is never idle.
The strategies discussed transform GPU expenditure from a runaway cost into a strategic asset that boosts your team's productivity and innovation.
Remember, the ultimate goal isn't just to spend less. It's to build a powerful, efficient infrastructure that empowers your teams to run more experiments and achieve results faster. In the competitive world of AI, the winner is never the one who spends the most, but the one who spends the smartest.




