Selecting drives for servers is a highly complex process. Enterprise hardware is very different from consumer hardware, at least in terms of durability. And when it comes to data storage drives, this is particularly important because they are storing commercially valuable or sensitive information. The loss of such data is a significant financial and reputational loss, as well as other negative consequences.
When choosing storage for a dedicated server, there are at least three key parameters to consider:
-
Reliability. The drive should be fault-tolerant and able to operate for long periods of time under commercial operating conditions.
-
Performance. The speed of reading and writing, the volume of requests processed per second have a direct impact on the comfort and quality of working with the server.
-
Response time. The response to the user's request should be fast, so that the user does not have to wait long for a response from the server, even under high load.
There are three types of storage devices used in a dedicated server: HDD, SSD and NVMe. In this article, we will review the main aspects of these storage devices and discuss the criteria for selecting a drive for specific tasks.
HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
The HDD (hard disc drive) most commonly found in personal computers, but can also be used in server systems. The device is well established and technically almost unchanged. The device is based on the principle of reading data from magnetic metal discs at an enormous speed (15,000 revolutions per minute).
Depending on the model, HDDs are equipped with 2 to 4 reading heads, which has made it possible to increase the speed of data reading. In general, however, speed is a weak point of these devices.
The fact is that the head finds information by means of the constantly rotating spindle. If the data is not stored in one sector of the disc, but in different sectors, the final search time increases.
Read/write speeds are also not fast enough for today's realities. With an empty hard drive and at least 128MB of cache memory, the machines deliver around 200Mbps. When the hard drive is full, the speed drops to 80-100 Mbps, which is critically low for business.
Another point: the HDD is very sensitive to external influences. Any serious vibration or shock can damage the magnetic platters and lead to a loss of information.
But HDDs are cheap, the maximum capacity has exceeded 20TB, and there are a huge number of devices from different manufacturers on the market. Including enterprise class. Such devices are suitable for cold storage, but it is not recommended to use HDDs for more complex tasks.
Advantages
-
Capacity. HDDs have a high storage capacity compared to SSDs and NVMe. This makes them ideal for storing large amounts of data.
-
Cost. HDDs are more affordable in terms of cost per gigabyte, which can be an important factor if you are on a tight budget.
Disadvantages
-
Read/write speed. HDDs are slower than SSDs and NVMe. This can affect overall system performance, especially when performing data-intensive operations or loading applications.
-
Fragility. HDDs are sensitive to external influences.
Applications
HDDs are ideal for cold storage of large amounts of data such as files, databases and archives.
They are used in situations where high capacity is required at a reasonable price and speed is not a primary consideration.
SSD (Solid State Drive)
SSD is a relatively new and therefore technically more advanced type of storage device based on flash memory (the same as traditional flash drives). This approach has solved most of the problems that existed in the HDD era.
What are the advantages of SSDs? They have no moving mechanical parts, are more compact and have incredibly reliable memory controllers that guarantee a working cycle of over 1 million hours. The risk of data loss due to mechanical damage is also reduced.
Because the data in SSDs is static, it takes ten times less time to search for the information required. SATA 3.0 provides up to 500 Mbit/s read and write speeds on the standard HDD interface. It is the high read and write speeds that have made SSDs truly effective devices for storage systems, cloud infrastructure and so on. They are energy efficient and offer a variety of system connection options: SATA, SAS, PCI-E, M.2.
SSDs traditionally cost more than HDDs. Pricing is influenced by mining trends, where SSDs are used to mine certain types of cryptocurrency. Mining and the production of chips for computing devices also have an impact. These areas suffered during the pandemic and have not fully recovered.
Advantages
-
Read/write speeds. SSDs offer high data transfer speeds, making them ideal for applications that require fast access to data.
-
Reliability. SSDs have no moving parts, making them more reliable and resistant to physical damage.
Disadvantages
- Cost. SSDs are more expensive than HDDs, which can limit storage capacity when budgets are tight.
Applications
SSDs are ideal for applications that require high-speed performance, such as web servers, high-load databases and virtualisation.
Use where a balance between performance and cost is required.
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express)
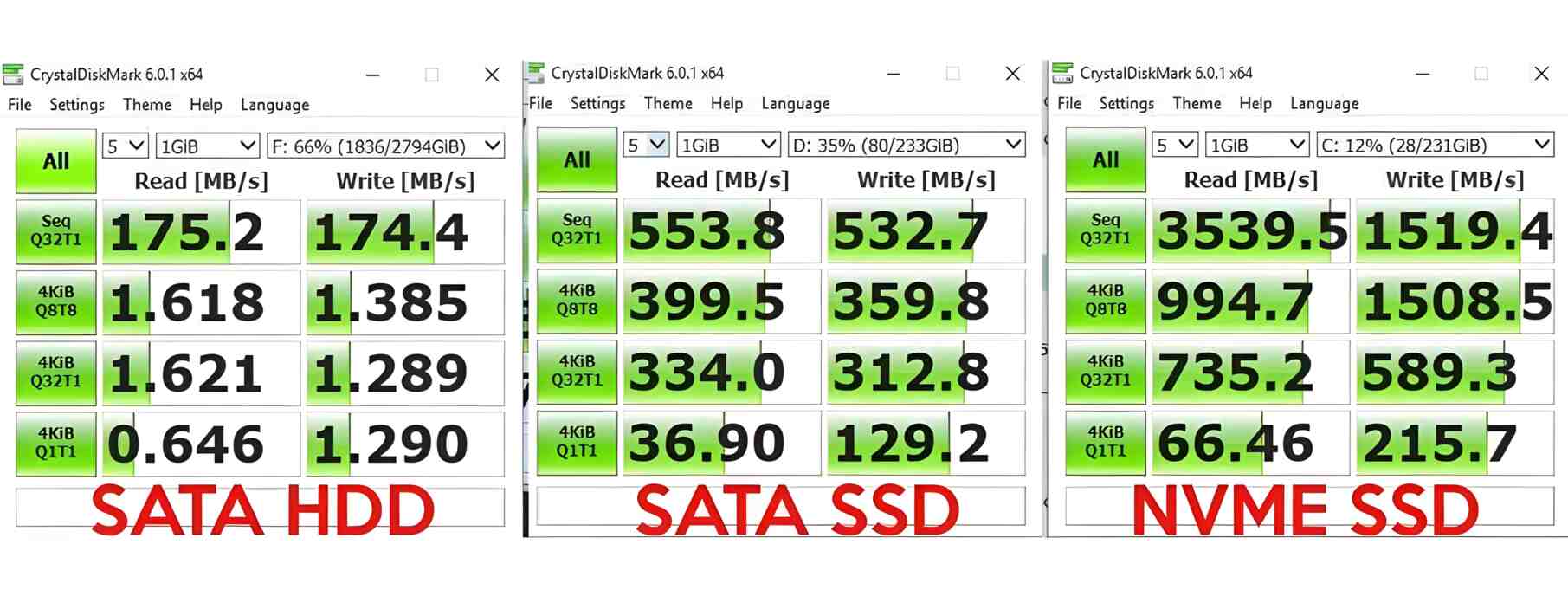
NVMe is the latest and fastest protocol for SSDs. It also uses flash memory, but the PCI-E 3.0/4.0 connection technology provides up to 7GB/s read and write speeds. This is up to 14 times faster than SATA 3.0. Each NVMe drive uses between 2 and 8 PCI-E lanes with a throughput of up to 2GB/s.
Another feature of NVMe is that the device communicates directly with the processor. In this way, the drives effectively solve the problem of read and write speeds, which is important to many businesses.
The main problem: the cost of the devices. NVMe SSDs use high-speed memory modules, and the chips and controller can heat up to 70-80 degrees. This requires a high-tech, efficient cooling system.
Such devices are not suitable for storage. But they are great for 3D rendering, CAD programs, working with neural networks, 4K and 8K content, and control software.
Advantages
-
Extreme speed. NVMe offers outstanding data transfer speeds, outperforming even most SSDs.
-
Low latency. NVMe offers minimal response time, which is especially important for applications that rely on low latency.
Disadvantages
- Cost. NVMe drives typically cost more than traditional SSDs, which can make them impractical for some projects.
Applications
NVMe is suitable for high-load applications such as large databases, data-intensive computing and high-volume virtual machines.
Ideal for situations where you need to maximise application performance.
Server drive connection interfaces
There are several types of server drive connection interfaces, each with its own performance, bandwidth and cost. The most common ones include
SATA (Serial ATA). SATA is one of the most common interfaces for connecting drives in home and small office systems. It provides a reliable and easy connection and is often used to connect HDDs and SSDs in small servers where high performance is not required.
SAS (Serial Attached SCSI). An evolution of SCSI technology, SAS offers higher bandwidth than SATA. It also supports the connection of multiple devices to a single controller. It is often used in enterprise server and storage environments that require high performance and fault tolerance.
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express). PCIe is an interface used to connect various devices, including NVMe drives. This interface provides the high bandwidth mentioned earlier. NVMe drives are connected via the PCIe interface to maximise performance. This option is often used in high load servers.
Fibre Channel. A high-performance interface designed to connect storage to servers. It provides high throughput and low latency. It is used in large enterprise environments where high performance and fault tolerance of data storage is required.
U.2 (SFF-8639). U.2 is an interface designed for connecting high-performance SSDs. It provides high bandwidth and supports connecting multiple devices to the same controller. U.2 is used to connect professional and enterprise SSDs, providing high performance when multiple devices are used simultaneously. U.3 is a further development of the U.2 format with the same dimensions but with additional pin groups on the connector.
Options for selecting different types of drives
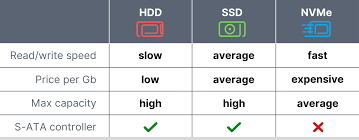
To make it clearer, here are a couple of examples of how to choose a drive (HDD, SSD or NVMe) for a dedicated server.
For storage of a large data array
Use SATA (SAS is better) drives in a RAID array. This option is not very expensive in terms of investment, but it is simple and reliable. Although the transfer speed is not high, it is acceptable for companies with 10-15 employees and low database load.
To minimize access latency
If reducing response time when accessing databases or a website is critical, we recommend choosing NVMe versions of PCI-E 3.0. SATA disks and SAS protocols cannot guarantee high speed, whereas NVMe can. Although it may cost more, it is the optimal option in terms of price and speed. This solution is used by some cloud providers and companies offering render farm services.
Latency Reduction and Hardware RAID
In this scenario, you need to use a SAS SSD. This gives you reasonable speeds of up to 12Gbps, support for multiple attached devices in parallel and the ability to combine multiple drives into a RAID array for greater reliability. Why SAS over NVMe: SAS is a more balanced solution for high access and high load environments. NVMe is susceptible to heat and should be handled more carefully.
Cost-effective file server
SATA HDD with capacities from 4TB and speeds of 5400 or 7200 RPM. The most cost-effective solution for a small business. There is a risk of data loss if the server fails.
High end file server
SAS SSD with capacities from 400GB without NVMe support. Cost-effective, stable option for businesses that are not using cloud solutions for whatever reason. High read and write speeds allow you to achieve the right level of comfort when working with the server.
The bottom line
There are obviously a lot of options for hardware combinations for a dedicated server. But when it comes to reliability, local solutions are usually inferior to popular cloud services. Not every company will be able to invest a large sums in the infrastructure, set up backups, data replication, a contingency plan and other issues that have long been known and solved by the technical specialists of cloud providers.
Enterprise hardware, more skilled engineers, real experience in dealing with a wide variety of situations - these factors also play into the favour of cloud service providers. These companies tend to use high-speed SSDs, which offer different levels of resilience and availability. Be sure to mention this when signing a collaboration agreement.


