Most companies' requirements for organizing remote work are perfectly met through desktop virtualization. Two technologies, VDI and RDS, are most commonly used. In this article, we explore their differences in terms of convenience, security, and flexibility.
VDI – (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) is an infrastructure for managing the users' virtual desktops that are hosted on a server. Traditionally VDI is a standalone dedicated desktop, yet RDS (terminal server or farm) is a specific type of VDI. The classic VDI solutions are Citrix Xen Desktop, Vmware Horizon, and Microsoft Remote Session Host Virtualization.
VDI and RDS are designed to accomplish a common goal – arranging remote work for employees. In addition, virtualization allows you to avoid the need to employ a large number of IT staff.
What is the difference between VDI and RDS?
The technologies are very similar in terms of functionality but have different implementations.
VDI is virtual desktops running on separate virtual machines, and each user's VM has its resources and can be different for different users.
Benefits of VDI over RDS:
- One virtual machine per user;
- Users, applications, and services are isolated and cannot influence each other;
- The ability to install complex professional software;
- Easily configurable user access policies.
RDS is a technology for organizing virtual desktops on one operating system and one virtual or dedicated server. In this solution, resources are shared among all users.
Benefits of RDS over VDI:
- Centralized maintenance of user desktops;
- One installation is enough to allow different users to use remote desktops;
- Less expense for software license purchasing, deployment, and maintenance.
Schematically, it works like this:
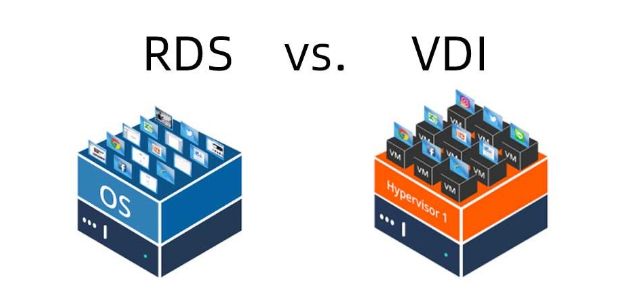
In the case of RDS, we have a VM/Physical Server with a Windows OS and RDS service deployed.
With Virtual Desktop Infrastructure, there is a VM/Physical Server with Windows, hypervisor, and services running the VDI infrastructure.
Making a choice
When choosing between VDI and RDS consider the following factors:
The number of users and the organization size. For example, with more than 400-500 users, RDS infrastructure may be slow and tough to maintain. For large organizations, it is better to consider VDI solutions.
Security and privacy requirements. VDI represents isolated VMs with an isolated OS, i.e. each user has its environment. In the case of RDS, all users work using the same OS, which has access to all user sessions.
Cost. The RDS is cheaper in terms of licenses and solution maintenance.
VDI architecture
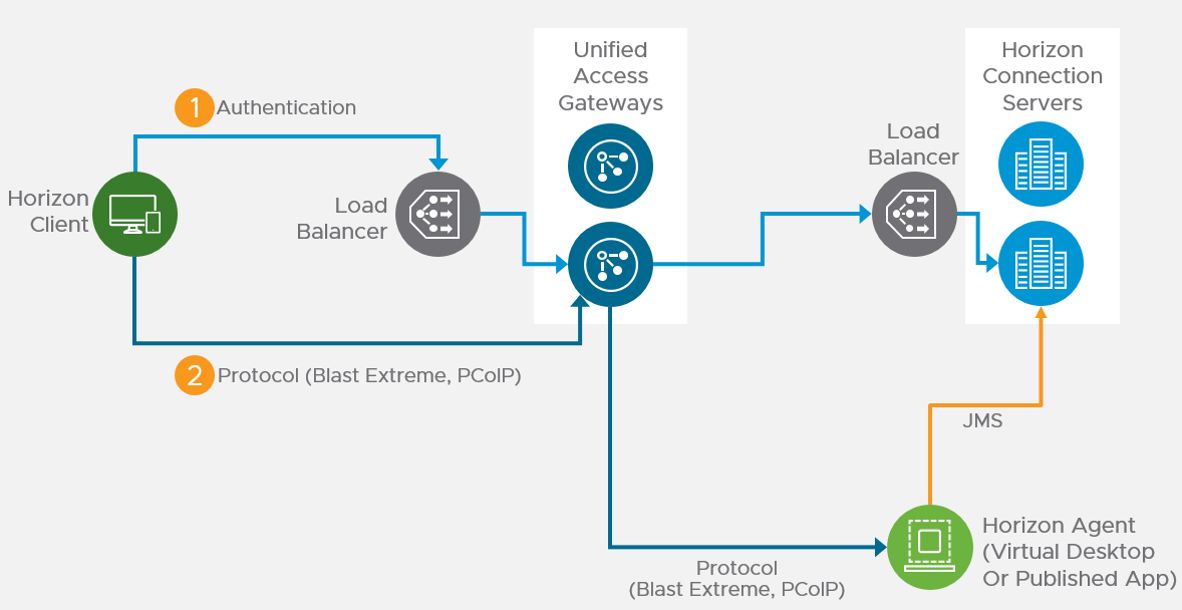
VDI (Citrix, VMware, Microsoft RDSH) presents a scheme with connection brokers, as well as VDI image management servers, and balancers. Here is the VMware Horizon scheme as an example. Each client finally gets a separate desktop within a separate VM.
A common architecture for a typical RDS terminal server
In an RDS scheme, users work within a single RDSH server or server farm.
Conclusions
Deploying workstations in the cloud allows you to allocate exactly the amount of resources that are enough to meet your current needs, and if necessary, quickly increase the capacity.
If you need a more flexible cloud infrastructure, you can create a hybrid solution by adding the required number of isolated virtual machines to a single RDS environment. Deploy VDI if you have at least 100 or more employees. It is important to have no more than 50 virtual machines per terminal server. We recommend combining all the terminal servers into one failover cluster.
Before you start implementing VDI or RDS technology, consider the parameters of the physical hardware and software. Think about the workload and application software, the number of concurrent sessions, and the total number of users. The more precisely you specify your requirements, the more comfortable it will be for the employees to use a virtual desktop.